 Honeysuckle as an ornamental plant has long been used in landscape design, and as a fruit crop grown relatively recently. Berries are becoming increasingly popular among gardeners, due to its beneficial and healing properties. Today we talk about honeysuckle varieties Violet, her landing and the intricacies of care.
Honeysuckle as an ornamental plant has long been used in landscape design, and as a fruit crop grown relatively recently. Berries are becoming increasingly popular among gardeners, due to its beneficial and healing properties. Today we talk about honeysuckle varieties Violet, her landing and the intricacies of care.
- Breeding history
- Description of the variety
- Bushes
- Berries
- Specifications
- Where to plant honeysuckle?
- How to care for a grade
- Watering and soil care
- Top dressing
- Pruning
- Pest and disease control
- Wintering varieties
- Advantages and disadvantages
Breeding history
Violet - the fruit of the breeders of the Pavlovsk Experimental Station (St. Petersburg), obtained by pollination of seed material varieties Roxana.
The study of the varietal characteristics and methods of reproduction for the introduction of the variety into the rows of cultivated crops was carried out by the experimental station of the Institute of Horticulture in the village Krasnutotsk, Kharkiv region. The authorship belongs to: A. V. Kondrikova, M. N. Plekhanova, V. A. Kibkalo.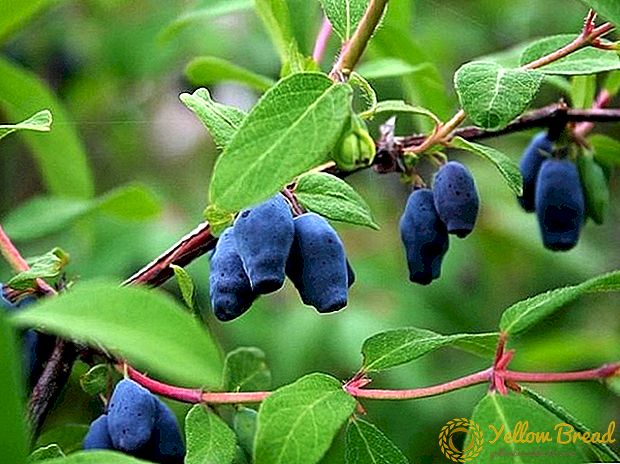 
The state test of the variety was carried out in 1992, after three years approval and recommendation was obtained for cultivation in all regions of Russia, as well as in Ukraine.
Description of the variety
Honeysuckle edible varieties Violet can perform on the site a dual function: fruit and ornamental plants, the bush is very beautiful in bloom, and during fruiting.
Bushes
Compact bushes with a lush crown rounded shape grow up to one and a half meters. Stems brownish-pink shade with a thick pile grow straight. The foliage is thick, sessile on short petioles, arranged in pairs. The leaf is broadly oval in shape with a soft tip and a clear, pale longitudinal strip dividing the leaf in half lengthwise. The color of the foliage is not bright green, the upper half is smoother, the bottom is slightly rough.
Blooming, the bush shoots long flower stalks with two flowers, flowers up to 2 cm in diameter, pale pink with five reed petals.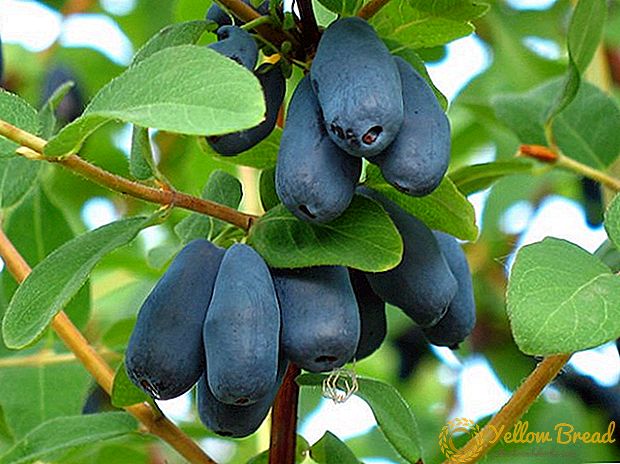 
Berries
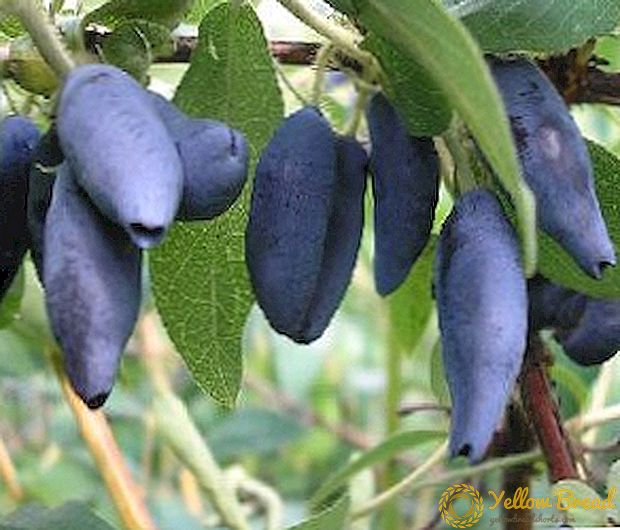
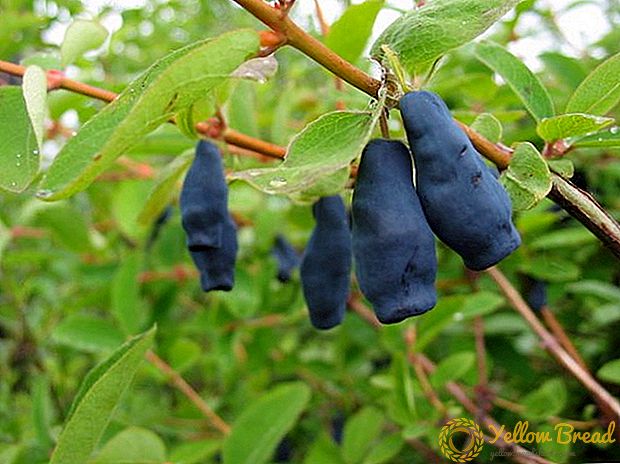
In late May, the berries of the plant ripen. They have an unusual shape: oblong, tuberculate with a concave recess at the end. Their length is up to 3 cm, and the maximum weight is 1.5 g. The color of the fruits of the ink shade with a slight wax coating. The flesh is covered with dense skin, fleshy with lots of fibers, taste sweet and sour, it smells good.
Specifications
- Taste qualities: in different years 4.7 - 5 points.
- The chemical composition of the plant: copper, selenium, manganese, iodine, A C, P, PP, glucose, fructose, organic acids.
- Pollination: cross.
- Varieties of pollinators: Amphora, Viola, Blue spindle, Morena, Nymph.
- Fruiting: in the third year after landing.
- Productivity: up to two kilos from a bush.
- Fruit precipitation: weak.
- Transportation: great
- Viability: resistant to diseases, little affected by insects, easily tolerates frosts.

Where to plant honeysuckle?
It is recommended to plant the plants at the end of the summer, until the second decade of November. In the spring, the plant starts sap flow early, so transplanting or planting is not desirable. Honeysuckle violet - perennial, it is better to immediately think of a permanent place to avoid frequent transplants, the place must be thought out for several plants at once.The bush is cross-pollinated, for subsequent fruiting it needs a suitable pollinator company.
For landing a quiet place, sheltered from drafts, but not in the shade: Honeysuckle loves the sun. Consider the location of groundwater, at least one and a half meters from the surface. Too close a location provokes the rotting of the root processes.

The distance between the bushes when planting at least one and a half meters, so that with the growth they do not obscure each other.
How to care for a grade
The care of the plant includes a standard set of procedures for moistening, feeding and caring for the soil and the appearance of the bush. What is important to know is that Violet does not like waterlogging and mineral fertilizers.
Watering and soil care
Watering should be regular, but moderate portions, in the heat of the bush you need to "water" daily, enough buckets of water under the bush. If there is regular rainfall, reduce watering. After watering, when moisture is absorbed, carry out weeding and loosening, they are necessary for the destruction of weeds and the access of oxygen to the roots. Do not forget to add a liter of ash directly to a bucket with water once a year in one of the irrigations to reduce the acidity of the soil. 
Top dressing
After the snow melts, as soon as the plants start to wake up, make nitrogen for the growth and development of green mass: 1 tbsp. urea in a bucket of water under the bush. In late spring, organic fertilizers are applied under the shrub: a bucket of humus or compost, an infusion of mullein.
In the autumn they also fertilize with organic matter, the floor of a bucket of compost or humus plus double superphosphate of 40 g. Consider the first years of honeysuckle enough fertilizing planted in the planting hole, fertilizers begin in the third year of life. 
Pruning
Sanitary pruning is carried out annually in early autumn: remove old, damaged or broken branches, cut off the shoots growing inside the crown.
When planting, many plant seedlings are shortened, in the case of honeysuckle, this should not be done, Violet will be significantly delayed with the entry into fruiting.
They form a crown at the age of six, conducting anti-aging procedures every 2-3 years. After removing damaged or dry branches, remove the lower tier of the branches, especially those that do not bear fruit. Usually leave about five main trunks. 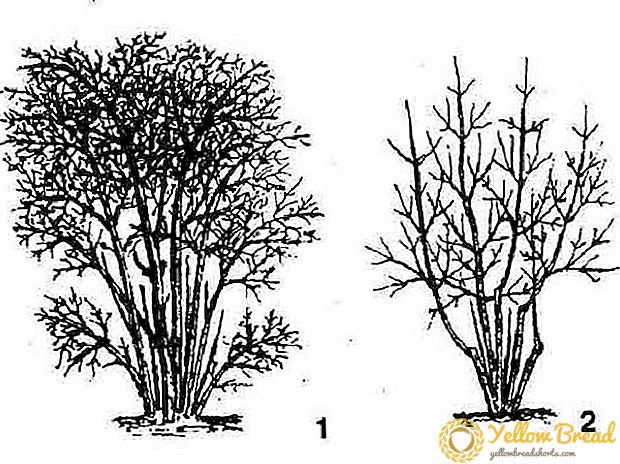
Shrubs, which are over twenty, begin to bear fruit worse, they are rejuvenated with cardinal pruning. Gradually, over several years, trunks that do not have fruit-bearing branches are completely cut off.
Pest and disease control
Violets pests: leafworms, caterpillars (they eat the green part), aphid and shieldweed (they feed on sap). To combat insects, you can use the following drugs:
- "Fitoverm";
- "Lepidocide";
- "Actofit";
- "Iskra-bio";
- "Bicol".
 These drugs are biological, that is safe for humans and domestic animals, as well as for insect pollinators. As prevention, spraying with "Konfidor", "Decis" or "Aktara" is carried out in early spring.
These drugs are biological, that is safe for humans and domestic animals, as well as for insect pollinators. As prevention, spraying with "Konfidor", "Decis" or "Aktara" is carried out in early spring.Very rare cases of powdery mildew, here you should also refer to safe drugs, such as Fitosporin and Baktofit.
Wintering varieties
In late autumn, the site where bushes grow is removed from fallen leaves and branches - this, by the way, is also a good preventive measure against pests, many of them hibernate in plant debris. If you have performed mulching on a wheel circle, the remnants must also be carefully removed. 
In principle, the honeysuckle does not need a shelter for the winter. It perfectly tolerates frosts of up to -50 ° C, even the buds do not die at -8 ° C.
Rodents are not interested in the honeysuckle bark, but birds can do harm: they are attracted to the plant's buds. Therefore, for safety reasons, they are covered with a dense mesh or burlap.
Advantages and disadvantages
Honeysuckle Violet is woven from the merits, in the description of the variety there are no significant shortcomings. Its main advantages are:
- frost resistance;
- not whimsical in care;
- rare diseases;
- small list of pests;
- transported easily and without loss;
- fructifies well;
- berries are large, with excellent taste characteristics;
- ripening is not showered.
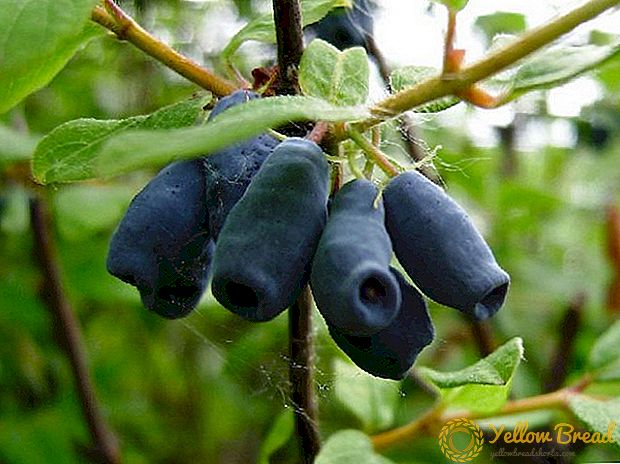

Honeysuckle, in addition to all the listed advantages, also has valuable medicinal qualities, in particular, ascorbic acid in its composition will help to significantly improve the immune system.






