 Many gardeners plant in their plots beautiful annual or perennial herbaceous plants - asters. There are more than 500 species. Asters are planted in flower beds, used for borders, rabatok, to decorate balconies or terraces, to compose beautiful bouquets and flower arrangements. But, unfortunately, all this beauty can be spoiled by the diseases of asters, with which more than one gardener has encountered.
Many gardeners plant in their plots beautiful annual or perennial herbaceous plants - asters. There are more than 500 species. Asters are planted in flower beds, used for borders, rabatok, to decorate balconies or terraces, to compose beautiful bouquets and flower arrangements. But, unfortunately, all this beauty can be spoiled by the diseases of asters, with which more than one gardener has encountered.
- Diseases of asters, treatment and prevention
- Jaundice asters
- Mealy dew
- Blackleg
- Asters rust
- Septoria
- Late blight
- Fusarium
- The main pests, methods of dealing with them
- Meadow bug
- Spider mite
- Passed Slug
- Sunflower fire
- Kidney aphid
- Drooling pennitsa
- Scoop gamma
- Thrips
- Earworm
Diseases of asters, treatment and prevention
Today, the seeds of asters are imported from abroad, and this increases the possibility of the emergence and spread of new viral diseases. New viruses and diseases that previously lived in other conditions quickly adapt and adapt to new ones.Asters, by themselves, suffer from a large number of viral diseases (24 species).
Jaundice asters
Aster pests such as cicada and aphids carry jaundice. The leaf plate suffers. First, it begins to turn pale along the veins, after which full chlorosis of the leaf occurs. Buds stop growing and turn green. To combat the disease should be sprayed with a solution of Anti-Vir or Pyrimora from pests.
 Against aphids, you can use a decoction of yarrow: 800 g of yarrow, pour 10 liters of water (boiling water) and boil for 2-3 hours, cool. Be sure to burn damaged plants. As a preventive measure, spray from pests that transmit viral diseases.
Against aphids, you can use a decoction of yarrow: 800 g of yarrow, pour 10 liters of water (boiling water) and boil for 2-3 hours, cool. Be sure to burn damaged plants. As a preventive measure, spray from pests that transmit viral diseases.
Mealy dew
Mealy dew is a fungal disease of asters. Its characteristic features are white bloom, drying and dropping of leaves, curvature of peduncles and their death. Often the disease spreads due to lack of nutrients, neglect of planting and high humidity.
To combat the disease:
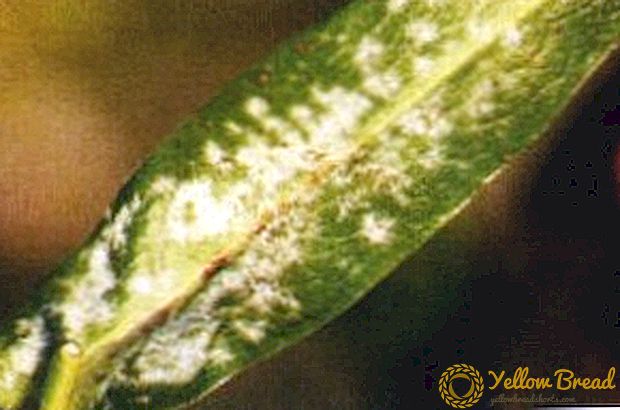 It should use drugs such as Topaz or Vectra, which are aimed specifically at fighting it;
It should use drugs such as Topaz or Vectra, which are aimed specifically at fighting it;- spraying should be carried out three times every two weeks.
Blackleg
Blackleg is a fungal disease that is the reason why asters blacken. Saplings and seedlings begin to turn black, the root neck and stems rot, the root rot begins, after which the plant dies. This fungus is common on acidic soils.
To combat the disease:
- conduct an early picking;
- remove large plants;
- disinfect the soil with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate;
- Sprinkle the soil around the asters with sand;
- Disinfect the drawers, hotbeds, flower pots with bleach or copper sulfate solutions.
 In order to get rid of the fungus, the soil should be watered with infusion of onion peels: 20 g of peels should be poured with a liter of boiling water and left for 24 hours, sieved and 2-3 sprays should be taken every week.
In order to get rid of the fungus, the soil should be watered with infusion of onion peels: 20 g of peels should be poured with a liter of boiling water and left for 24 hours, sieved and 2-3 sprays should be taken every week.Asters rust
A disease like the rust of asters can cause the death of all the flowers in the area. Spores of rust are carried by the wind over long distances, and they tolerate wintering well, and in spring they strike healthy flowers again.
Rust is manifested by the appearance on the leaves of spots and growths of brown and brown color. If you do not start fighting with this disease in time, it will quickly spread to other flowers.
To combat rust and to prevent:
- Plant asters away from coniferous trees (250-350 meters);
- carry out preventive spraying Bordeaux fluid;
- if rust has already appeared - spray fungicides every two weeks until the complete elimination of the disease.
Septoria
 Another reason why asters disappear is Septoria. This disease is characterized by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves, which spoil the appearance of asters. The disease spreads quickly and affects all the leaves, they shrink, aster stops growing and dies.
Another reason why asters disappear is Septoria. This disease is characterized by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves, which spoil the appearance of asters. The disease spreads quickly and affects all the leaves, they shrink, aster stops growing and dies.
To combat the disease:
- thin out the landings;
- spray a solution of Bordeaux liquor or copper oxychloride.
Late blight
Another fungal disease that asters are exposed to is late blight. Distinguished by the appearance of brown spots and white bloom.
To combat the disease:
- should be sprayed with preparations containing copper;
- remove remnants of damaged plants.
Fusarium
Fusarium is one of the most dangerous diseases. It is caused by the fungus Fusarium, which is spread by spores. Infected plants through the soil. The disease penetrates the vasoconducting system and clogs it, after which Fusarium wilt occurs.
To combat the disease:
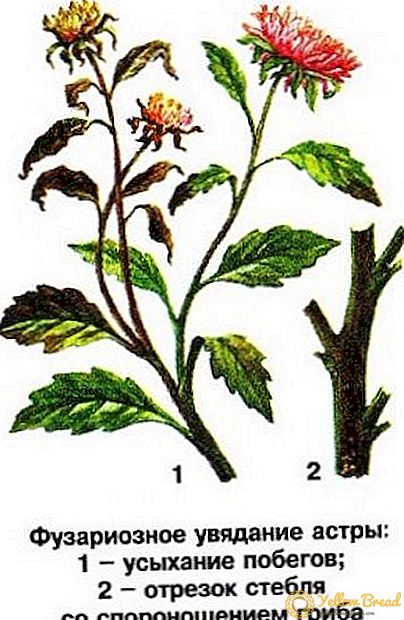 it is necessary to alternate cultures when planting;
it is necessary to alternate cultures when planting;- add lime to the soil to maintain neutral acidity;
- Steam the soil before sowing seeds;
- To prevent seedling disease, after planting, spray plants with a solution of copper oxychloride.
The main pests, methods of dealing with them
Pests of asters bring a lot of trouble to gardeners. In addition to spoiling the beauty of plants, they also carry diseases with viruses. In order to protect the flowers from harmful insects, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures:
- autumn digging of the earth;
- removal and destruction of dead plants and annuals in the autumn;
- correct location and choice of landing site;
- apply humus, lime and compost to the soil;
- the correct distance between the plants.
Meadow bug
 The size of the bug is only 5-10 mm, however, it can cause great damage to flowers. The bug is a yellow insect with an elongated body, to which the wings are tightly pressed. The bedbug damages flowers, buds, shoots, leaves and stems. The leaves begin to curl, the buds are deformed.The pest is very active from June until the end of flowering, especially during dry periods.
The size of the bug is only 5-10 mm, however, it can cause great damage to flowers. The bug is a yellow insect with an elongated body, to which the wings are tightly pressed. The bedbug damages flowers, buds, shoots, leaves and stems. The leaves begin to curl, the buds are deformed.The pest is very active from June until the end of flowering, especially during dry periods.
Pest Control:
- spraying with karbofos solution;
- phosphamide dusting.
Spider mite
A tick is a pest of 0.4-0.5 mm in size that lives on the underside of a leaf. Its color in spring and autumn is orange-yellow, red, and in summer - green-yellow. He eats the juice of asters, because of which the leaves turn yellow and fade.
Pest Control:
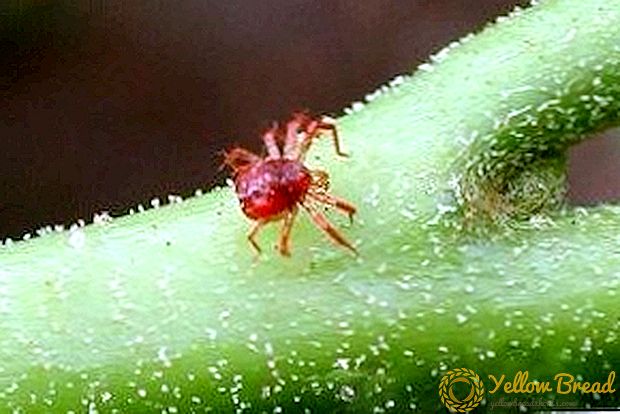 weed control;
weed control;- watering with a solution of sulfur and lime in dry weather;
- spraying with 2% pyrethrium solution, 0.2% solution of karbofos, tincture of tobacco, garlic or onion.
Passed Slug
Slug eats leaves and damages the buds. It can be easily recognized by the elongated slimy body with horns on the head. The slug reserves the oblong holes covered with its secretions.
Pest Control:
- carry out the destruction of weeds;
- sprinkle with lime on the borders of the plots;
- process the soil with lime.
Sunflower fire
 This pest is a butterfly with a size of up to 20-25 mm. Wings gray, elongated. Caterpillars reach sizes 9-15 mm. Butterflies are dangerous because they lay eggs on the anther of flowers. Caterpillars eat pollen and flower petals, then move and eat seeds in flower baskets.
This pest is a butterfly with a size of up to 20-25 mm. Wings gray, elongated. Caterpillars reach sizes 9-15 mm. Butterflies are dangerous because they lay eggs on the anther of flowers. Caterpillars eat pollen and flower petals, then move and eat seeds in flower baskets.
Pest Control:
- soil treatment with basudin before planting;
- collecting caterpillars and butterflies by hand.
Kidney aphid
 Aphid mainly damages young plants. It feeds on the sap of the plant, which is why the leaf plates start to curl, dry up and fall off. Aphids can spread to asters from nearby plants or the weeds on which she lived. Therefore, if you are spraying asters, spray the nearest plants for prevention.
Aphid mainly damages young plants. It feeds on the sap of the plant, which is why the leaf plates start to curl, dry up and fall off. Aphids can spread to asters from nearby plants or the weeds on which she lived. Therefore, if you are spraying asters, spray the nearest plants for prevention.
Pest Control:
- spraying bushes karbofos;
- spraying drug Inta-vir.
Drooling pennitsa
These yellow-green larvae live in frothy secretions on leaves or sprouts. Activity is manifested from mid-May to early July. They damage the leaves and stems of flowers. This leads to deformation of asters and a decrease in its flowering.
Pest Control:
- carry out treatment with Karbofos or Antio;
- use for spraying infusion or decoction of tobacco with soap.
Scoop gamma
 The scoop-gamma is a medium-sized dark-brown butterfly, which is distinguished by a light icon on its wings, resembling the Greek letter gamma. It causes great harm in the spring when young plants appear. In the second half of summer, the butterfly is less dangerous. Caterpillar scoops green, length 32 mm, on its back 8 light lines. Caterpillars eat above-ground parts of plants.
The scoop-gamma is a medium-sized dark-brown butterfly, which is distinguished by a light icon on its wings, resembling the Greek letter gamma. It causes great harm in the spring when young plants appear. In the second half of summer, the butterfly is less dangerous. Caterpillar scoops green, length 32 mm, on its back 8 light lines. Caterpillars eat above-ground parts of plants.
Pest Control:
- carry out the destruction of weeds;
- spraying of plants with a solution of Chlorophos, Karbofos, Phosphamide.
Thrips
Thrips cause great damage to the leaves of plants. Eating leaves, they cause yellowing, drying and dropping of leaves. The appearance and decorativeness of asters is lost.
Pest Control:
- Spray the extract of onion, tobacco and garlic peels.
Earworm
 The body of earwig ordinary resin-brown color, up to 2 cm long. An adult insect is harmful to plants. Shows activity from the second half of June until the end of flowering. Due to the earwig activity, the leaves, buds and inflorescences of asters are damaged.
The body of earwig ordinary resin-brown color, up to 2 cm long. An adult insect is harmful to plants. Shows activity from the second half of June until the end of flowering. Due to the earwig activity, the leaves, buds and inflorescences of asters are damaged.
Pest Control:
- to carry out dusting with pyrethrum, basezol;
- manual collection followed by the destruction of the pest.
Thus, to ensure good flowering and a healthy type of asters, care should be taken to protect them from pests and diseases. Do not forget about the methods of prevention that will help avoid wasting money on expensive drugs and chemicals.

 It should use drugs such as Topaz or Vectra, which are aimed specifically at fighting it;
It should use drugs such as Topaz or Vectra, which are aimed specifically at fighting it; it is necessary to alternate cultures when planting;
it is necessary to alternate cultures when planting; weed control;
weed control;




