 All garden crops, including cabbage, are prone to disease. It is much easier to carry out preventive measures against infecting them than to cure acquired ones. Moreover, some of them can not be treated.
All garden crops, including cabbage, are prone to disease. It is much easier to carry out preventive measures against infecting them than to cure acquired ones. Moreover, some of them can not be treated.
- Bacterial and viral diseases of cabbage: symptoms and control methods
- Mucous bacteriosis
- Vascular bacteriosis
- Cabbage mosaic
- Fungal diseases of cabbage: symptoms and ways to fight
- Alternaria (black spot)
- White rot
- White rust
- Quila
- Downy mildew (perinospora)
- Mealy dew
- Rhizoctoniosis
- Gray rot
- Dry rot (fomoz)
- Black leg of cabbage
- Late blight
- Fusarium wilt (tracheomycosis)
- Cabbage disease prevention
Bacterial and viral diseases of cabbage: symptoms and control methods
The whole edible part of the cabbage is above the ground, therefore, processing with pesticides to kill cabbage diseases means harming one’s own health. Poisonous substances that are dangerous to the human body, being absorbed into the leaves, accumulate there and remain forever. Therefore, prevention, especially folk methods, is always preferable.
Mucous bacteriosis
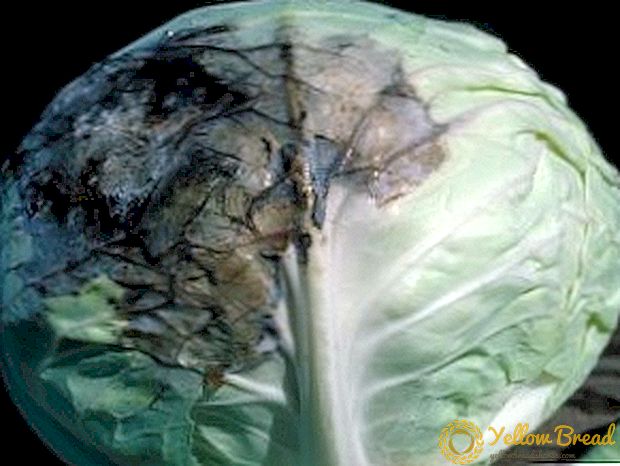 Such a disease of cabbage as mucous bacteriosis occurs mainly during storage, when the temperature regime is significantly elevated. The disease develops due to bacteria and proceeds in two ways: the outer leaves rot, an unpleasant smell emanates from them, then the stalk begins to rot; the second option - begins rotting from the head, mucus is formed, then leaves are affected. Opportunities of the disease contribute to too large doses of nitrogen, heavy rainfall or watering, non-compliance with crop rotation. For the prevention and control should:
Such a disease of cabbage as mucous bacteriosis occurs mainly during storage, when the temperature regime is significantly elevated. The disease develops due to bacteria and proceeds in two ways: the outer leaves rot, an unpleasant smell emanates from them, then the stalk begins to rot; the second option - begins rotting from the head, mucus is formed, then leaves are affected. Opportunities of the disease contribute to too large doses of nitrogen, heavy rainfall or watering, non-compliance with crop rotation. For the prevention and control should:
- grow hybrid varieties that are immune to the disease,
- eliminate pests throughout the season,
- do not disturb crop rotation
- disinfect the crop where it is stored,
- observe temperature storage conditions
- process the seeds before planting,
- process the roots of seedlings ("Fitoflavin-300").
Vascular bacteriosis
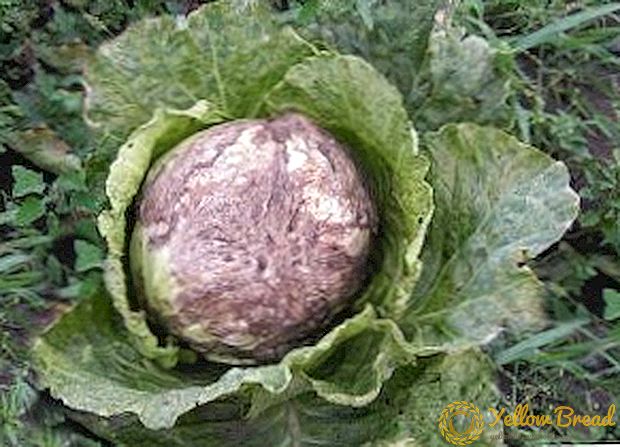 Cabbage bacteriosis occurs at any stage of development: the disease falls on a plant with insects or during rains. Manifested by yellowing of the affected leaf, then streaks turn black on it. Subsequently, the leaves darken completely and die.The problem is that a viable bacterium remains in the soil for up to two years. Control and prevention measures:
Cabbage bacteriosis occurs at any stage of development: the disease falls on a plant with insects or during rains. Manifested by yellowing of the affected leaf, then streaks turn black on it. Subsequently, the leaves darken completely and die.The problem is that a viable bacterium remains in the soil for up to two years. Control and prevention measures:
- To plant hybrids, they are more resistant;
- Plant in the same place at least four years;
- Time to remove weeds.
Cabbage mosaic
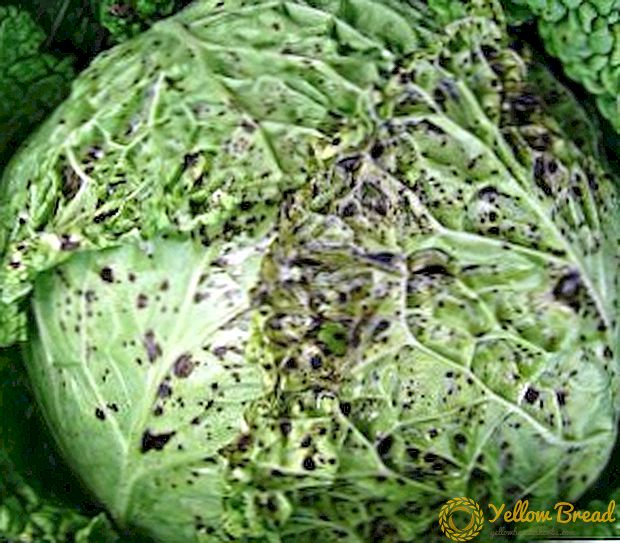 This viral disease is spread by weeds of the cruciferous family, affected by aphids. First, the cabbage streaks brighten, then stop growing, and the leaf frowns. Prevention is to fight with aphids and weeds, the disease can not be treated. Affected heads must be dug and burned.
This viral disease is spread by weeds of the cruciferous family, affected by aphids. First, the cabbage streaks brighten, then stop growing, and the leaf frowns. Prevention is to fight with aphids and weeds, the disease can not be treated. Affected heads must be dug and burned.
Fungal diseases of cabbage: symptoms and ways to fight
Almost all fungi are diluted in a humid environment, with improper storage or neglect of seed disinfection or seedlings.
Alternaria (black spot)
Most often, the disease appears in the storage of seedlings and harvested crops. Black stripes and spots appear on the seedlings, which causes wilting. In adult plants, stains are accompanied by soot.Sometimes the plaque gets inside the head, which is also accompanied by spots that turn on the leaves. Preventive actions: hydrothermal treatment of seeds or their treatment with TMTD, respect for crop rotation and timely removal of weeds. During the growing season can be treated with drugs containing copper.
White rot
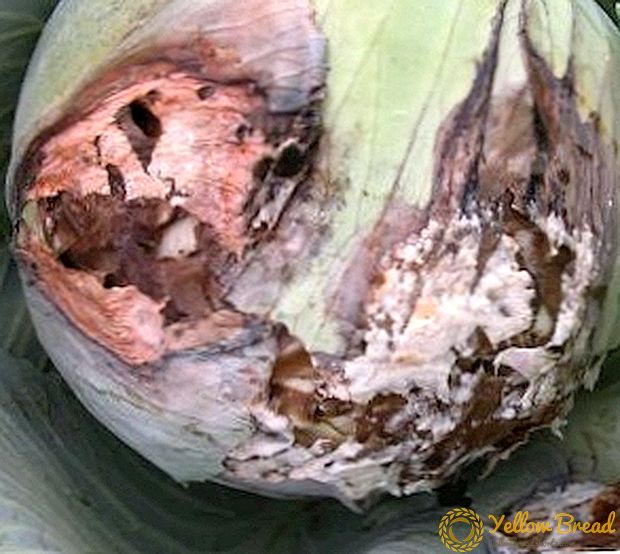 This disease develops in wet and cool weather, during the formation of the head. The main signs of the disease appear already in storage. Mucus appears on the leaves, and the black points of the spores of this fungus grow around the lesion.
This disease develops in wet and cool weather, during the formation of the head. The main signs of the disease appear already in storage. Mucus appears on the leaves, and the black points of the spores of this fungus grow around the lesion.
Prevention consists in disinfecting the storage facility; you only need to harvest in dry weather, leaving three centimeters of head in the ground and a couple of lower leaves. When an infection is found in the storage location, the affected areas are removed and covered with chalk.
White rust
The causative agent of the fungus is a parasite, which is bred on weeds. The development is helped by wet weather or the presence of water on the leaves. The affected parts of the cabbage become fleshy, the edges of the leaves curl. Prevention: the destruction of weeds, the treatment of soil from pests before planting.Seed plants can be sprayed with Ridomil Gold.
Quila
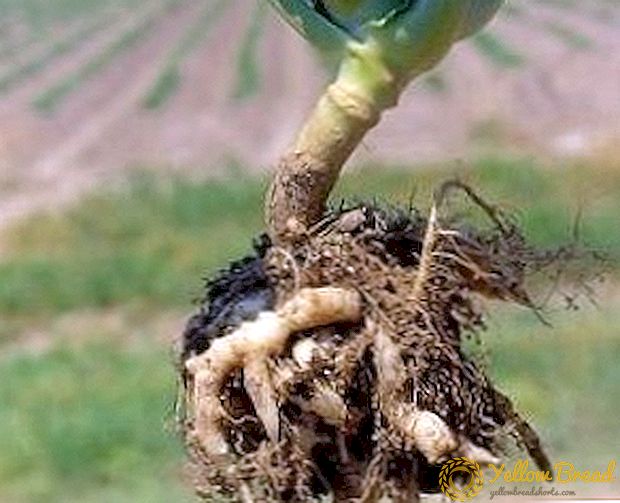 The causative agent of the keel in cabbage is the cystospores of the lower fungus that are stored in the soil. The cunning of the disease is that at an early stage it is difficult to notice. You can find it only by digging up cabbage, on its roots there will be growths of different sizes. A symptom of the disease - wilting of the leaves. The disease is spread in wet, cool weather, with affected seedlings. Therefore, before planting, inspect seedlings. To prevent damage from the keel helps the treatment of the soil with slaked lime, you can also use fungicides.
The causative agent of the keel in cabbage is the cystospores of the lower fungus that are stored in the soil. The cunning of the disease is that at an early stage it is difficult to notice. You can find it only by digging up cabbage, on its roots there will be growths of different sizes. A symptom of the disease - wilting of the leaves. The disease is spread in wet, cool weather, with affected seedlings. Therefore, before planting, inspect seedlings. To prevent damage from the keel helps the treatment of the soil with slaked lime, you can also use fungicides.
Downy mildew (perinospora)
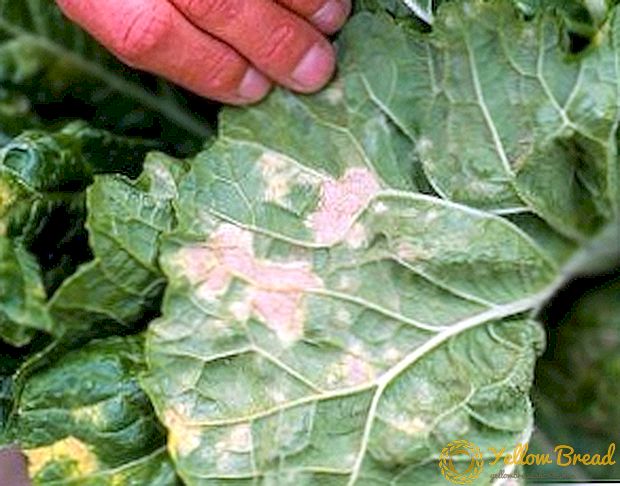 Infection with peronosporosis occurs through seeds or soil. Both seedlings and adult cabbage are sick. The first signs of the disease appear on young leaves in the form of yellow spots on the outside of the leaf. With the spread of the disease on the leaves appears gray putrid plaque - spores.
Infection with peronosporosis occurs through seeds or soil. Both seedlings and adult cabbage are sick. The first signs of the disease appear on young leaves in the form of yellow spots on the outside of the leaf. With the spread of the disease on the leaves appears gray putrid plaque - spores.
For prevention, treat the seeds before sowing, observe crop rotation. In the event of an illness, treat the cabbage "Fitoftorinom" - this is a biological product.
Mealy dew
Powdery mildew lesions are covered with white powdery powdery powder. Since the plaque is wiped off, like dust, many perceive it as well. There is a gray patina on the inside of the sheet, yellow spots appear on the outside. As soon as you notice something like this, start treating Fitosporin-M, use it once every three weeks until you get rid of the disease.
Rhizoctoniosis
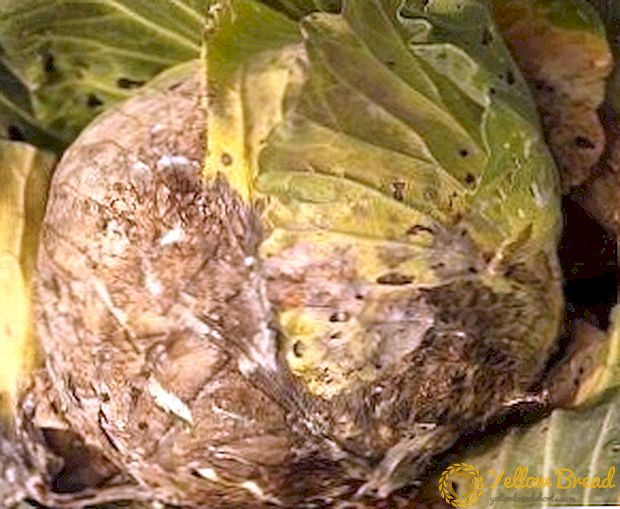 Damage occurs when soil gets on the leaves. First, orange-yellow specks appear, which gradually spread the infection to the whole plant, ulcers form on the leaf petioles, root cervix turn yellow, roots root, and the plant dies. When a disease occurs, spray the plant with a 0.2% solution of copper oxychloride. Preventive measures are to comply with the conditions of planting and development of cabbage.
Damage occurs when soil gets on the leaves. First, orange-yellow specks appear, which gradually spread the infection to the whole plant, ulcers form on the leaf petioles, root cervix turn yellow, roots root, and the plant dies. When a disease occurs, spray the plant with a 0.2% solution of copper oxychloride. Preventive measures are to comply with the conditions of planting and development of cabbage.
Gray rot
In this disease, the lesion occurs at the place of cabbage storage. Spores of the fungus thrive in high humidity, inhabiting the cabbages of fluffy mold, while the cabbage leaves are in black spots. Preventive measures:
- During the period of growth to monitor watering, it should be moderate;
- Do not overdo it with nitrogen supplements;
- Remove dry and yellowed leaves from the head;
- Disinfect before storing the crop.
Dry rot (fomoz)
Phonosis of cabbage is manifested by white spots with dark patches on the leaves of cabbage. You can confuse with a black leg, but with this disease the sick areas are gray, and the underside of the leaf is lilac. Here the methods of spraying "Fitosporin-M" of the affected areas help, and for prevention, before sowing, treat the seeds with Tigam 0.5%.
Black leg of cabbage
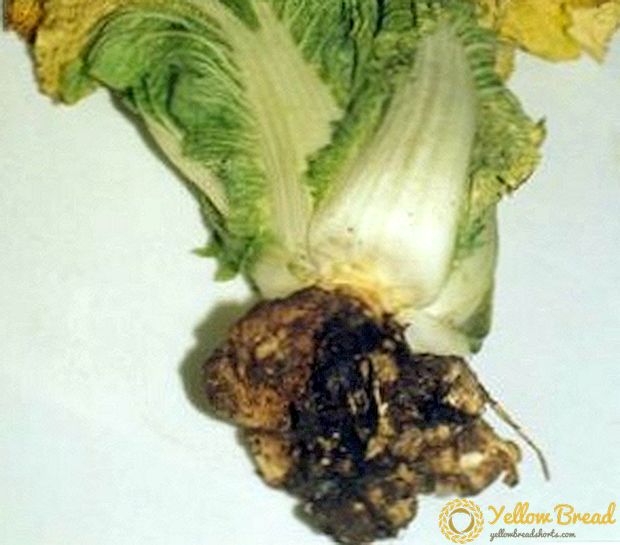 Cabbage black leg is a rather dangerous infection, it is important to figure out how to deal with this fungus, because it multiplies very quickly. The causative agent of the disease is in the soil and feels good with an increased level of acidity and humidity. Cabbage is the most susceptible, too often planted and overfed with nitrogen fertilizers. Sick plants dry out, the root neck becomes thinner, and the lower part of the trunk rots on the seedlings of the affected fungus.
Cabbage black leg is a rather dangerous infection, it is important to figure out how to deal with this fungus, because it multiplies very quickly. The causative agent of the disease is in the soil and feels good with an increased level of acidity and humidity. Cabbage is the most susceptible, too often planted and overfed with nitrogen fertilizers. Sick plants dry out, the root neck becomes thinner, and the lower part of the trunk rots on the seedlings of the affected fungus.
Before planting, it is necessary to decontaminate the soil with 1% potassium permanganate solution, treat the seeds with "Fundazole" or "Planriz". Unfortunately, there is no cure: diseased plants are cleaned, burned, and the soil is disinfected with marcinate.
Late blight
If infected with late blight, the fungus spreads from the stem to the leaves, affecting the head. The shoots covering the head become dark brown. Between the leaves affected white fluff spore. Yield loss with late blight - 50% of the fruit.
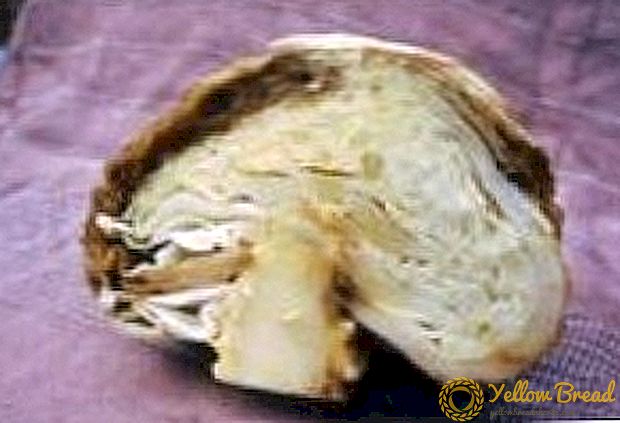 How to handle cabbage in this case is not yet known. There are only preventive measures: compliance with crop rotation, disinfection of soil and seedlings, and you should not plant bulbs near
How to handle cabbage in this case is not yet known. There are only preventive measures: compliance with crop rotation, disinfection of soil and seedlings, and you should not plant bulbs near
Fusarium wilt (tracheomycosis)
The popular name is jaundice, as with this disease the leaves turn yellow and are not tied to the head. Even if it is fastened, it will be a shriveled, skewed plant with fallen bottom leaves. This infection can kill most of the crop.There are no methods to combat this disease of cabbage. For prevention, diseased plants are removed and the soil is treated with manganese solutions with potassium or copper sulfate.
Cabbage disease prevention
Before planting, it is possible and necessary to carry out preventive procedures, at this stage it is possible to use chemical compounds that are contraindicated during the period of plant development. It is better to use less aggressive natural products, but they are not as effective., if we consider that in most cases, the means of controlling cabbage fungal diseases are not found. Often it is necessary to destroy adult plants. Natural varieties are more susceptible to diseases; Hybrids, respectively, are less frequently affected, and if all the conditions of planting and storage are met, the weather conditions (minimum moisture) are not affected by plants.
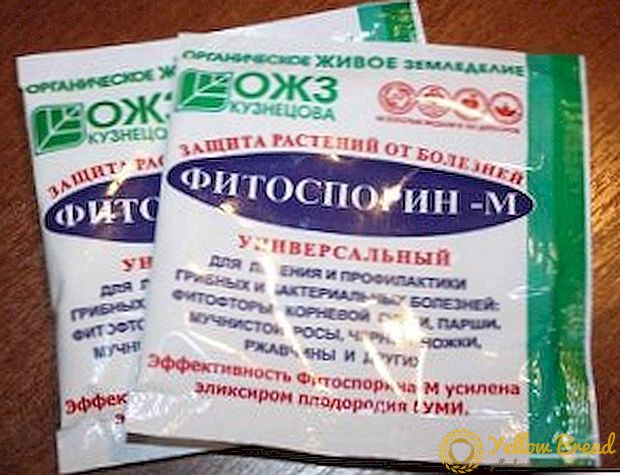 Disease prevention includes a set of procedures. In the autumn after harvesting the soil must be thoroughly dug, then treated with chemical or folk remedies. Chemicals: Cumulus DF, Fitosporin; natural broths from hot pepper, horsetail or upright marigolds.
Disease prevention includes a set of procedures. In the autumn after harvesting the soil must be thoroughly dug, then treated with chemical or folk remedies. Chemicals: Cumulus DF, Fitosporin; natural broths from hot pepper, horsetail or upright marigolds.
Important for the prevention of proper crop rotation, that is, the alternation of different crops in one place. Thus, the soil is less depleted, and the plants are less exposed to diseases. In order to protect young seedlings in the early stages of its development, it is necessary to add up to 50 g of wood ash to the well. This should be done directly during the landing in the soil. During development, you can treat Planriz, Baktofit or Fitoflavin-300, which are not dangerous for our health.
Cabbage is a great vegetable, you can cook a lot of dishes from it, you can eat raw and drink cabbage juice, which is very useful for the stomach, used as a filling for pies and pies, maintain strength and vitamin level during diets.






