 Goat breeding is one of the most profitable areas of animal husbandry. Products goat production include meat, milk, wool, down and skins. The main advantage of goats lies in their high adaptability, so goat breeding at home will not cause you much difficulty.
Goat breeding is one of the most profitable areas of animal husbandry. Products goat production include meat, milk, wool, down and skins. The main advantage of goats lies in their high adaptability, so goat breeding at home will not cause you much difficulty.
- How to choose a goat
- Dairy breeds
- Downy
- Conditions of detention
- Spring, summer, autumn
- In winter
- Feeding the goats
- How to make a diet
- Examples
- Proper milking
- Breeding and lambing
- Major Diseases
How to choose a goat
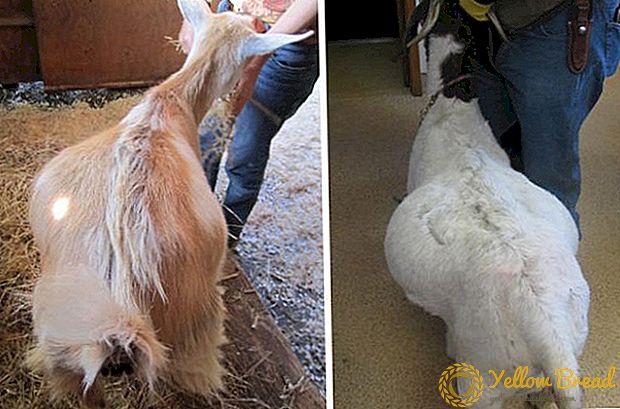
It is necessary to approach the choice of a goat with all responsibility. You must be able to independently assess the condition of the animal, to determine its age. The following are recommendations for proper selection of dairy and downy breeds.
Dairy breeds
When buying dairy breed inspect the appearance of the animal. Dairy goats must have:
- light and thin head medium size;
- well formed bones;
- wide chest;
- straight back;
- flat, stable and widely set limbs;
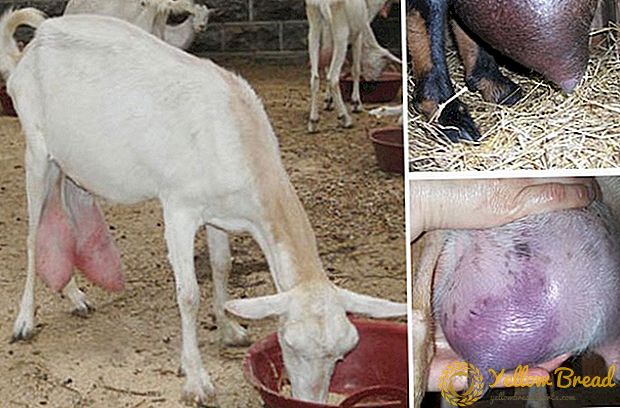
- pear-shaped or spherical, elastic to the touch and not sagging udder;
- well developed nipples.
 Among dairy breeds, Zaanenskaya is considered the most productive. This breed is the largest and is characterized by high precocity, fertility and high-quality milk.
Among dairy breeds, Zaanenskaya is considered the most productive. This breed is the largest and is characterized by high precocity, fertility and high-quality milk.Downy
Let us turn to the criteria for the selection of representatives of downy breeds. Consider the requirements for appearance:
- the large size of the animal (the larger the body area, the greater will be the rune);
- large girth of the chest behind the shoulder blades;
- smooth lines of the back and sacrum;
- wide loin;
- strong straight legs;
- small head;
- uniform obrosly body;
- the hair on the head should not be stiff, better when it hangs over the eyes;
- skin without folds;
- suit white color.

Conditions of detention
Goats are distinguished by good health and excellent adaptation to any conditions. Breeding and maintenance of goats at home will not be difficult even for novice breeders.
Spring, summer, autumn
In the spring, after the cold weather, the goatlings thoroughly clean. At the time of cleaning the premises goats are placed in a dry place with a canopy. The litter on which the animals were kept is replaced.
The walls, floor and stall of the milk goat are washed with heated water with soda and laundry soap. After washing the room is thoroughly aired, dried. The walls are lime white.
In spring and summer, in favorable weather, the animals spend the whole day on a walking tour. The cattle begin to be driven out to pasture after the dew has dried and the grass is rooting. Initially, goats graze on elevated and warmed areas.  Before the beginning of the grazing, animals, if necessary, cut the hair around the eyes. Also, cattle should be plenty to drink so that animals do not drink contaminated water from puddles along the way.
Before the beginning of the grazing, animals, if necessary, cut the hair around the eyes. Also, cattle should be plenty to drink so that animals do not drink contaminated water from puddles along the way.
Goats do not tolerate high temperatures. Direct sunlight is a nuisance to animals, and can also lead to thermal shock. With the onset of heat goats are driven out to pasture as early as possible, at dawn.
In hot weather, the goats stand with their heads down, trying to hide in the shade. Therefore, on hot days, it is necessary to pause from 10-11 to 14-16 hours. With the onset of evening coolness, grazing is resumed and continues until dark.
Young goatlings are also taken out for grazing, but on cold spring days they are looked after, not allowing them to lie down on the ground and forcing them to move more.  Goats are also sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure, so in rainy weather or before rain, it’s better not to graze. With a single grazing animal must be tied. To do this, use the usual collar.
Goats are also sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure, so in rainy weather or before rain, it’s better not to graze. With a single grazing animal must be tied. To do this, use the usual collar.
In the fall, the cattle is transferred to stall. The transitional stage lasts about 7-10 days. The first days of the animals are fed in the morning with hay, then driven out to pastures. After a few days the amount of hay is increased.
In winter
In winter, cattle must be taken daily for a walk. Walking should last at least 3-4 hours, because with limited movement deteriorates the well-being of animals and their reproductive function deteriorates.
Walking is especially necessary for downy breeds. They easily withstand low temperatures, especially in calm weather. Representatives of downy rocks longer hold on the open air.
Feeding and watering are allowed in the pen, only in the rains and snowfalls the cattle are fed in the barn.
If there is not much snow (the height of the snow cover does not exceed 12-14 cm), and the temperature outside is 12 ° C, you can resort to pasture-walking mode of keeping.  Winter grazing helps hardening of adult animals and better growth of the young. After the soil freezes, floodplain meadows are good places for grazing.
Winter grazing helps hardening of adult animals and better growth of the young. After the soil freezes, floodplain meadows are good places for grazing.
In the case of ice crust formation on snow, before walking the site it is better to break through, so that the animals do not hurt themselves and can easily get forage from under the snow.
For winter grazing is suitable light forest or shrubs. The goat is a neat animal.Before feeding, the cattle must be released from the pen for emptying the bowels.
In winter, goat hair and skin are quickly polluted. Animals need to be brushed daily. Do this with a comb and a stiff brush. When combing removes excess hair with parasites. Wool gets a smooth and elastic look.
In addition, cleansing facilitates breathing and improves skin blood circulation, which affects the down productivity. With winter watering, the beard of goats gets wet and frosting, so it must be cut off regularly.
Feeding the goats
Goat is a rather unpretentious ruminant pet. Feeding these amazing creatures is not difficult, they are happy to eat almost any food, which makes their breeding quite profitable.
How to make a diet
In order to increase the productivity of goats and get healthy offspring, the diet of animals must be complete and contain all the necessary elements. The main food of goats is grass in summer and hay in winter.The grass should be juicy and nutritious, and hay should be of high quality.
Dairy breeds of goats produce up to 8 liters of milk per day, while consuming a lot of energy. Therefore, it is necessary to feed such goats abundantly and correctly.
- Summer goat diet. Goat grazing eats about 8 kg of grass per day. But animals should be additionally fed with grain and legume concentrates. It is undesirable to feed the goats with whole grains. Grain concentrates are barley, corn, oats; legumes - peas, lentils. Grain milled or give in the form of finished feed at the rate of half a kilogram per day per head.
During the period when grass on pastures burns out and dries out (approximately from the middle of July), livestock must be fed with vegetables or branches. Also goats are happy to eat kitchen waste. 
- Winter diet of goats. Hay is a coarse feed needed by the body of ruminants. Therefore, goat hay is recommended to give plenty. Hay is desirable to take deciduous. It is allowed to partially replace brooms or straw, but they are less nutritious.
- for the female - 1.8-2.2 kg;
- for the male - 2.5-3 kg;
- for young stock - 0.8-1 kg.
 The following is the rate of consumption of feed and concentrates per head. In the year on one animal you will take:
The following is the rate of consumption of feed and concentrates per head. In the year on one animal you will take:- roughage - 350 kg for young, 550 kg for milch goat;
- juicy feed - 400-600 kg;
- concentrates - 30-40 kg.
Compound feed can be given both in liquid form and in the form of thick porridge. In order not to spoil the beneficial supplements and vitamins, do not brew purchased food boiling water. Compound feed goats eat from 0.5 to 1 kg per day. Mixed with mixed fodder is recommended to cook and give kitchen waste. Partial replacement of bran feed is allowed.
Do not forget about salt and vitamins. Even with proper nutrition for prevention, it is recommended to add vitamins to animal feed (especially high-yielded and sugynous goats).
Today, the market presents a huge variety of vitamin preparations. For example, "Trivit", "Tetravit" or various premixes. A month before the lambing, water the female "Kaiodom" (1 tablet once a day).  Salt is desirable to use iodized.The amount of salt per head is 8-10 grams or 1 teaspoon. Salt can be given in the form of lick. Also give the animals chalk, bone meal and brooms.
Salt is desirable to use iodized.The amount of salt per head is 8-10 grams or 1 teaspoon. Salt can be given in the form of lick. Also give the animals chalk, bone meal and brooms.
Try not to mix everything at once. When using the premix, vitamins should not be given separately; only salt.
For the manufacture of brooms young shoots are cut, tied in bunches and hung in a dark ventilated room. The first few days you need to turn the brooms over so that they are better blown out and dry.
Brooms for goats can be harvested from any trees and shrubs. Fruit crops are especially valuable. The only exceptions are poisonous rocks.
But, in addition to standard branches, corn stalks and nettle are good material for making brooms. Brooms, let's up to 5 pieces per day.  As for the watering of the goats, animals should be guaranteed free access to the water or they should be watered during each meal. Give the goats only clean water. In winter, the water should be warm or room temperature.
As for the watering of the goats, animals should be guaranteed free access to the water or they should be watered during each meal. Give the goats only clean water. In winter, the water should be warm or room temperature.
Examples
Approximate diet for feeding goats in summer:
- In the morning, give compound feed or soaked bran.
- After milking, release the cattle to pasture, preferably with access to water.
- In the evening, give feed and succulent feed - potatoes, pumpkins, carrots, cabbage leaves, apples.
- At night, so that the animals have something to chew, put a little hay.
- As mineral supplements, give chalk with bone meal (12 g per day per head). Do not forget about the water - it should always be in animals in the public domain.
It is necessary to feed the goats in the winter (stall) period 3 times a day at a strictly defined time. Approximate diet:
- In the morning, give half the fodder (feed, vegetables, or waste from the table, as well as hay and brooms).
- In the afternoon, give us succulent feed, as well as hay and brooms.
- In the evening - feed, roughage, hay.
Proper milking
A good dairy female can produce from 5 to 8 liters of milk per day. But it is important to learn the right milking technology. With each animal you need to act individually.
Milking begin one month before lambing. Gradually massage the udder, trying not to cause pain. Just before the lambing, the massage is stopped, otherwise the goat will not allow it to be milked.  If the female has a good state of health, the first milking can be carried out an hour after lambing.If you keep a goat for milk, the offspring is better to immediately select and feed artificially.
If the female has a good state of health, the first milking can be carried out an hour after lambing.If you keep a goat for milk, the offspring is better to immediately select and feed artificially.
Before milking a goat, be sure to water it with warm water. To make the goat stand still, you can give her a favorite dish (a piece of bread, an apple).  When milking, maintain udder hygiene. To do this, just wash it with warm water and wipe dry. For many adult females, this event becomes familiar.
When milking, maintain udder hygiene. To do this, just wash it with warm water and wipe dry. For many adult females, this event becomes familiar.
Sitting under the goat is very uncomfortable, so it is advisable to arrange a low platform for milking. All manipulations spend soft, not sharp movements. For a good tide of milk, gently massage the udder.  Grab the nipple with all your fingers, squeeze and pull down. To clean the milk channels, the first streams must be decanted.
Grab the nipple with all your fingers, squeeze and pull down. To clean the milk channels, the first streams must be decanted.
Milk must be completely sown, since its residues can cause mastitis in animals. After milking, the udder should preferably be treated with an odorless softening agent. 
Breeding and lambing
The life expectancy of goats is 10 years or more. The reproductive abilities of animals directly depend on the care of the goats and what they were fed with.Individuals who have reached the age of one and a half years are allowed to the first case.
First you should familiarize yourself with the existing methods of mating and choose the most optimal one. Experienced herders use three basic methods: manual, free and harem mating. The most popular and reliable method - the acquisition of a goat-manufacturer.
Pregnancy is confirmed 2 months after mating, when the udder becomes slightly fuller, and when touched, the goat crouches. Succinating female looks calmer, moves smoothly and carefully.
In the sucrose goat, the appetite increases. Feed it needs more abundant. In the second phase of syagnos (pregnancy), add 10 g of crushed chalk per day. Milking stop for a month and a half before delivery, gradually reducing the number of milkings.  Pregnancy lasts 147-150 days. If you want to get two offspring a year, you can reattach a month after the lambing. However, this time can be missed, then the goat lactation will last.
Pregnancy lasts 147-150 days. If you want to get two offspring a year, you can reattach a month after the lambing. However, this time can be missed, then the goat lactation will last.
A couple of weeks before the lambing, clean the goat house, whiten the walls, warm the windows and doors, eliminate drafts. In the last days before the lambing, watch the uterus regularly, because in severe frosts, newborn babies can die.
If the female is well developed, childbirth takes 1-3 hours and does not require human intervention. A couple of hours after the lambing, the afterbirth departs.
Major Diseases
Consider the main non-communicable, infectious, invasive and parasitic diseases of goats and ways to assist animals:
- Acute timpania scar. It occurs due to a sharp change in the diet. As a result, there is intense gas formation in the rumen, belching is upset, the abdomen greatly increases in volume. The animal refuses to feed and can quickly die. The treatment consists of removing the gas from the scar and restoring the belching.

- Infectious mastitis - This is an udder disease affecting nursing goats. The disease can be acute or chronic. Udder increases in size, becomes painful and hot to the touch. The female gives less milk, then the milk production stops almost completely. Preventive measures: keeping animals in warm and cozy conditions, regular and high-quality feeding.
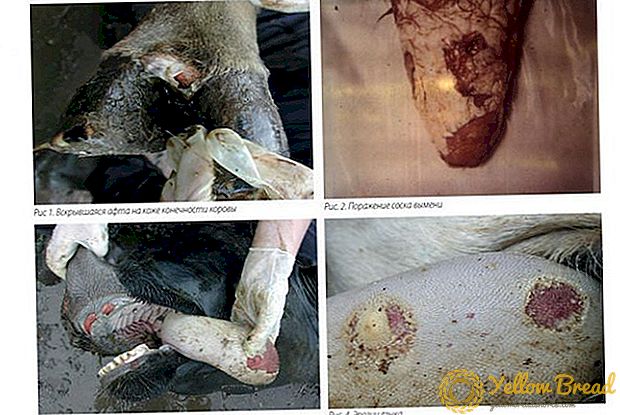
- Foot and mouth disease. The oral cavity, udder and hooves are affected (bubbles appear, lips swell, drooling is observed). The body temperature rises. The disease lasts a week. There is a high mortality rate among kids. Animals affected by foot and mouth disease are temporarily isolated, washed with disinfectants, give light food. Milk obtained from sick animals is boiled.
- Listeriosis The nervous system of goats is affected. Typical signs - loss of balance, circular movements, convulsions, seizures, head turned to the side. Death usually occurs after 10 days. Meat is eaten after two hours of cooking. The cattle are vaccinated and given antibiotics. Conducted thorough disinfection of premises.

- Leptospirosis. There is a sharp increase in body temperature of animals. They become sluggish or too agitated, the appetite disappears, there are convulsions and frequent urination (urine is red). Sick goats die within two days. Some animals can be cured, but because of the farm unsuitability they are allowed for meat.
- Fascioliasis - parasitic disease caused by fasciol larvae.Animals become infected on swampy pastures or standing bodies of water. The illness occurs in a chronic form, affects the liver and causes a disorder of metabolism. Animals look depressed, lose their appetite and often die from exhaustion. Treat fascioliasis with carbon tetrachloride. In order to prevent anti-parasitic therapeutic measures are carried out.

- Echinococcosis. Animals are infected by ingestion with food or water from mature cestodes that live in the intestines of carnivores (for example, dogs). In the stomach and other organs of the animal the larvae of the parasite form echinococcus (blisters). In the intestines, the larvae transform into mature nematodes. The affected organs of goats are destroyed. For prophylactic purposes, shepherd dogs are regularly dewormed.
- Zenuroz. Animals become infected with parasites in the same way as with echinococcosis. From the intestines, through the blood, helminth eggs penetrate into the brain of goats, where they form blisters. These blisters squeeze the nerve cells, after which the clinical symptoms of the disease appear. In sick animals, appetite is lost, goats linger for a long time in one place or whirl. Cattle perish from exhaustion.Medical treatment is performed by trepanning the skull and removing the blisters. Sometimes the bubbles are pierced and the existing fluid is sucked out of them.

- Moniezioz. Most of the young are diseased. The disease is caused by tape nematodes that form in the small intestine. Infected livestock at sites with ticks. In sick goats, digestion is upset; animals quickly lose weight. Often, a blockage of the parasite causes the death of the animal due to blockage of the intestine. The treatment consists of deworming livestock. As a preventive measure, young animals are given a mixture of edible salt and copper sulfate.

- Dictyocaulosis - Another parasitic disease caused by filamentous worms accumulating in the lungs. Helminths lead to pneumonia, and then to severe malaise of the whole body. Animals die from exhaustion or asphyxia as a result of blockage of the respiratory tract by clusters of worms. For treatment resort to feeding the salt mixture.
- Piroplasmosis - blood-parasitic disease transmitted by ticks. Illness is accompanied by jaundice, increased heart rate and fever. Treatment consists of immunizing animals and taking medication.
A warm room in winter, grazing in warm weather, varied and full feeding, good care and care - this is what all goats need without exception, so that they delight us with healing milk and rich fluff.













